SARS-CoV-2 Spike – ACE2 Binding Assay Service for Inhibitor Screening
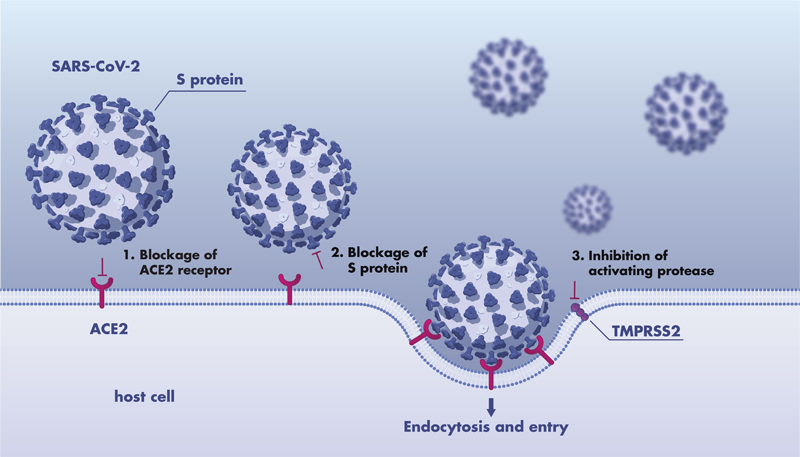
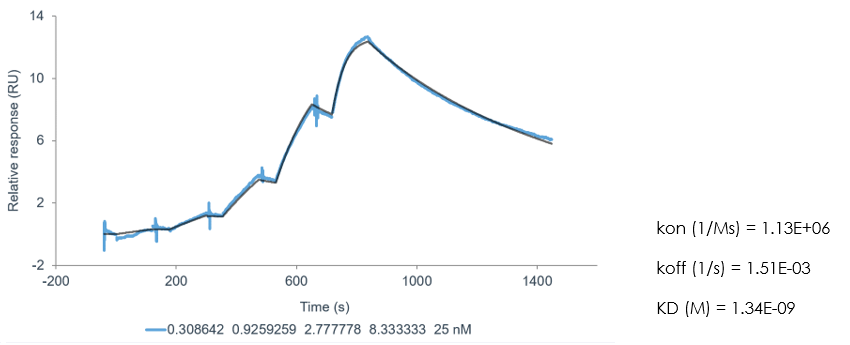
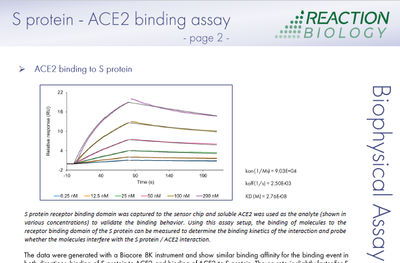
The SARS-CoV-2 Spike-ACE2 binding assay for inhibitor screening is performed with surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology measuring the direct binding of potential therapeutics to the Spike protein RBD (receptor-binding domain) or ACE2. The assay is suitable to determine whether a test molecule(s) inhibits the Spike-ACE2 binding for blocking of SARS-CoV-2 virus entry into host cells.
The SARS-CoV-2 spike-ace2 inhibitor screening assays can investigate two targeting strategies:
1. The development of molecules that occupy the host cell’s ACE2 receptors to block the virus from attaching to the host cell.
2. The development of molecules that bind and saturate the Spike protein on the virus surface such that binding to ACE2 is blocked.
The SPR assay technology allows to:
- Probe the direct binding kinetics (on/off-rate and KD) to optimize target engagement (on-rate) and residence time on the target (off-rate)
- Inhibitor screening of new drug candidates with a throughput of up to 2300 compounds per day.
Our SARS-CoV-2 Spike-ACE2 inhibitor screening service is available for pharmaceutical companies and medical researchers around the world. Read our blog to learn more about the advantages of this assay: Biophysical characterization of compounds disrupting the SARS-CoV-2 Spike – ACE2 interaction using SPR