PDGFR-beta Cellular Phosphorylation Assay (intracellular kinase activity assay) for compound screening and profiling in intact cells
The mitogenic signaling in mammalian cells is carried out mainly by growth factors that interact with receptors localized at the plasma membrane. Most of these receptors have a tyrosine kinase activity domain that is localized at the cytoplasmic region of the molecule. The interaction of the growth factors with the receptors, besides inducing the kinase activity of the receptor, activate signaling pathways that alter gene expression patterns and induce mitogenesis, or if deregulated are related to cancer. Among these receptors PDGFR-beta has been characterized as target for directed therapy.
PDGFRB
JTK12, PDGFR, CD140B, PDGFR1, PDGFRbeta
NIH3T3
Endogenous
The murine fibroblast cell line NIH3T3 is known to overexpress the PDGFR-beta receptor tyrosine kinase. Stimulation of these cells with its physiological ligand Platelet derived growth factor (PDGF-BB), results in a robust receptor autophosphorylation. Compounds are preincubated before cell stimulation to allow thorough target binding. Stimulation conditions are optimized to determine dose-related inhibition of the phospho-PDGFR-beta signal, which is subsequently quantified by Sandwich-ELISA technique. The assay is validated based on known inhibitors of PDGFR kinase activity (see Fig. 1).
Substrate phosphorylation as a readout of intracellular kinase activity via ELISA
Freiburg, Germany
More information can be found on our website Cellular Phosphorylation Assay Services.
Reference compound IC50 for PDGFR-beta
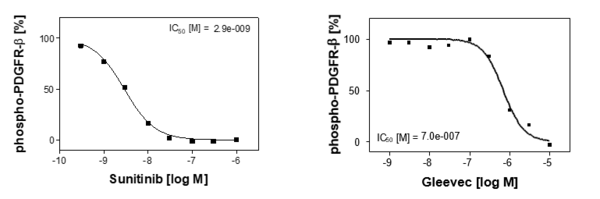
Sunitinib blocks PDGFR-beta as a general kinase inhibitor whereas Gleevec is known to inhibit the PDGF-BB-induced phosphoPDGFR-beta signal in a specific manner. Both compounds were included for the validation process and the cellular PDGFRbeta assay generated highly reproducible IC50 values. The graphs show representative results.