Mode of Action Analysis
After hit identification, the measurement of the activity on the actual target is essential to avoid chasing off-target effects. Such measurements can include:
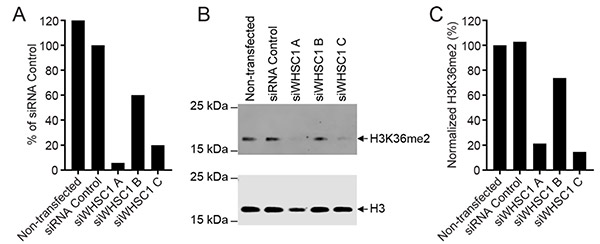
- Quantification of the target activity in cells, e.g., phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation
- Quantification of a downstream effect of a target, e.g., gene expression, protein degradation, or protein localization
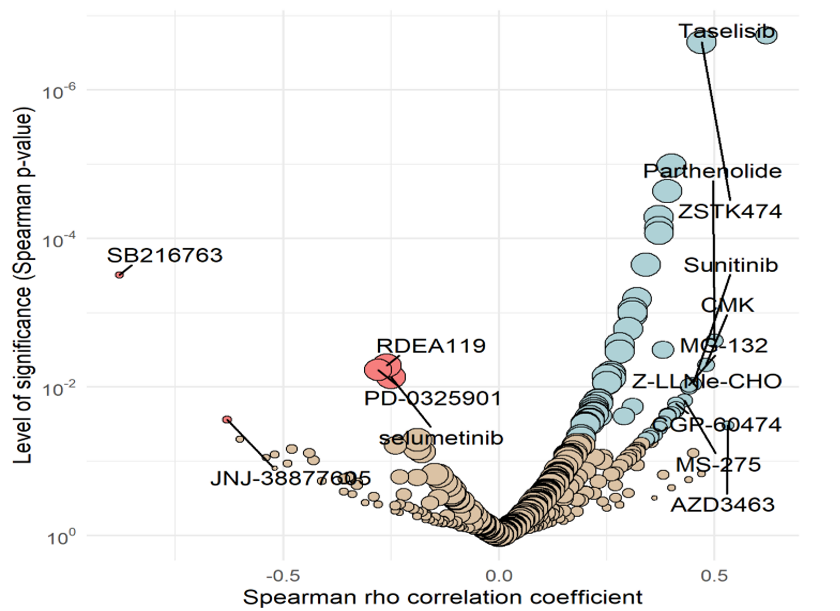
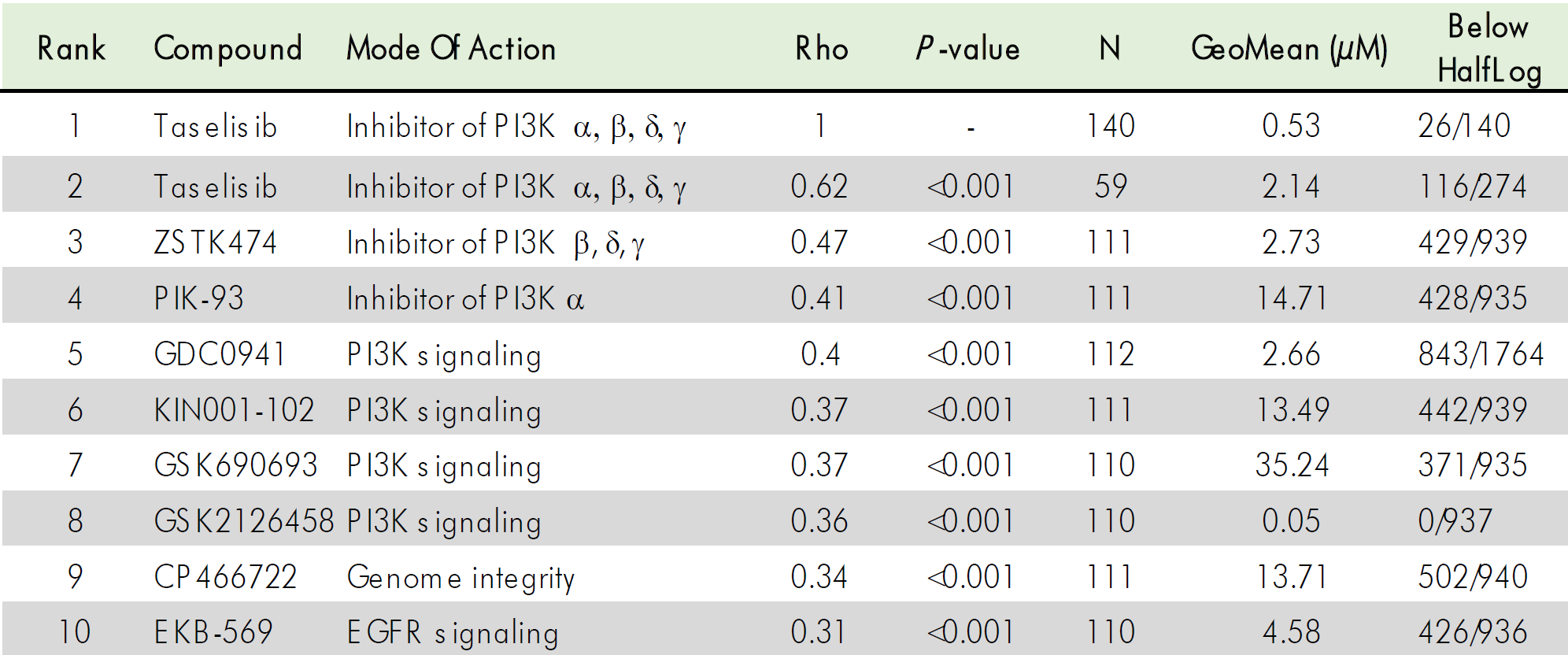
In a more holistic approach, the assumed mode of action of a new compound can be confirmed with our MoA Finder tool based on compound screening of cytotoxic effects on a large panel of tumor cell lines.
In most cancer drug discovery projects, the ultimate goal is the death of tumor cells. The investigation of the cell death mechanisms gives insight into the events downstream of target inhibition. We can examine various cell death mechanisms, including the accumulation of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, and apoptosis. Cell cycle arrest studies can aid the understanding of the mode of action.