Humanized Xenograft Models
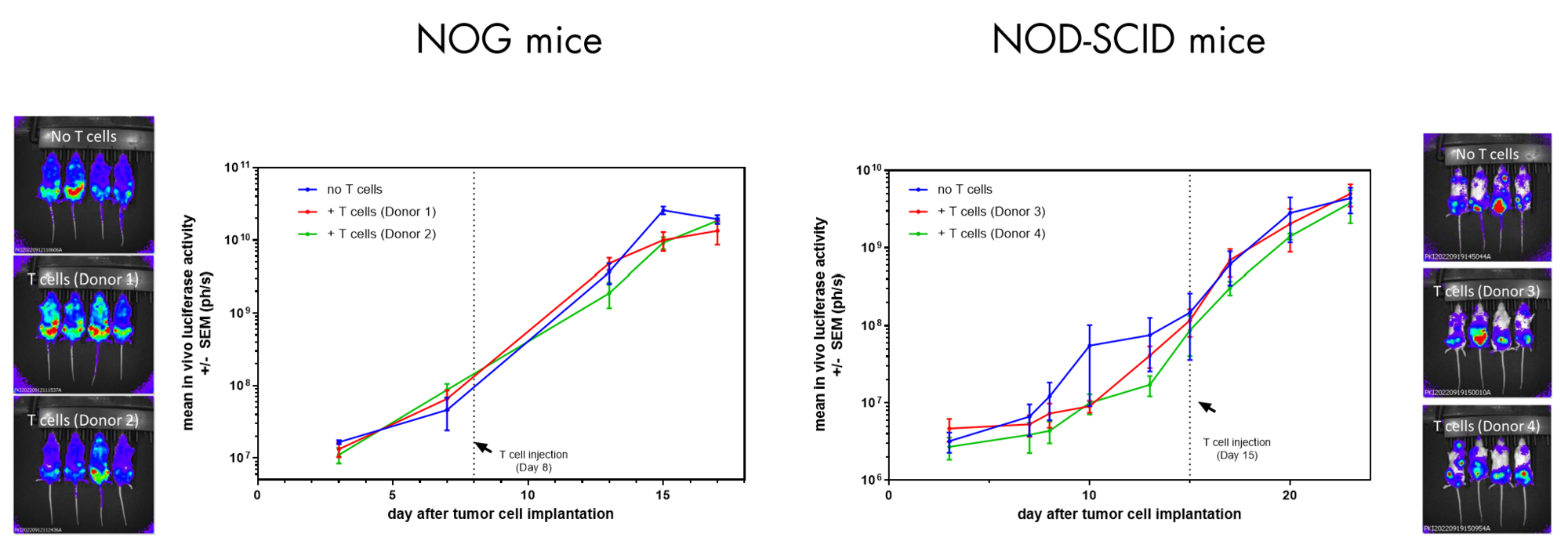
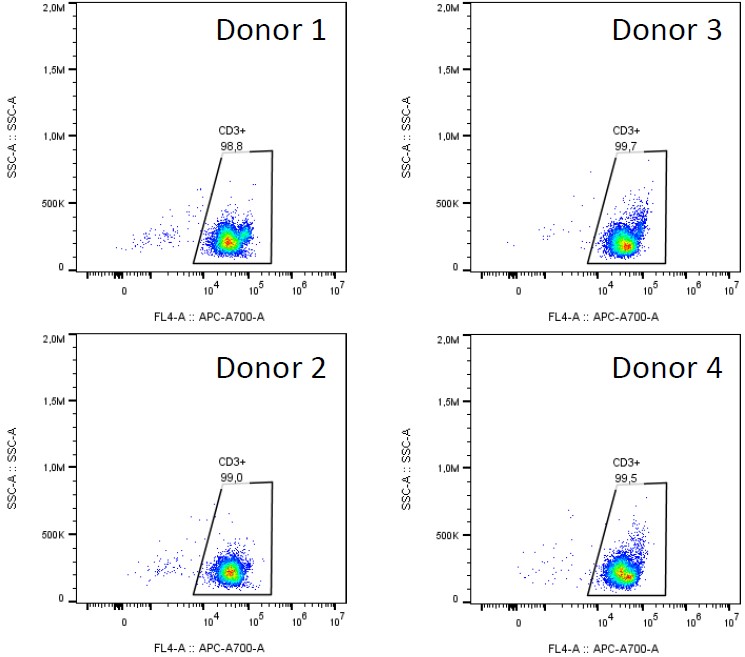
Humanized xenograft models recapitulate the interplay between the tumor and the immune system occurring in patients by engrafting human tumor bearing murine hosts with human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), T cells or NK cells.
These models enable rapid testing of human targeted immunotherapies and provide insights into a drug mechanisms of action, kinetics, toxicity, and potency.
Our team of immunology experts have developed a range of different humanized xenograft mouse models in which different components of the human immune system have been reconstituted to allow for the testing of efficacy and potency of your immuno-oncology drug candidate.
What we offer:
- A fully humanized platform to test human specific immunomodulators
- A simplified approach to humanization compared to humanized PDX
- A team of expert available to assist on study designs and data analysis
- T cell or NK cell reconstituted human tumor bearing models to evaluate your agent in vivo
- A diverse panel of human tumors-derived xenografts including AML and breast cancer
Reach out today to discover how our platform can help you advance your human immunotherapy research.